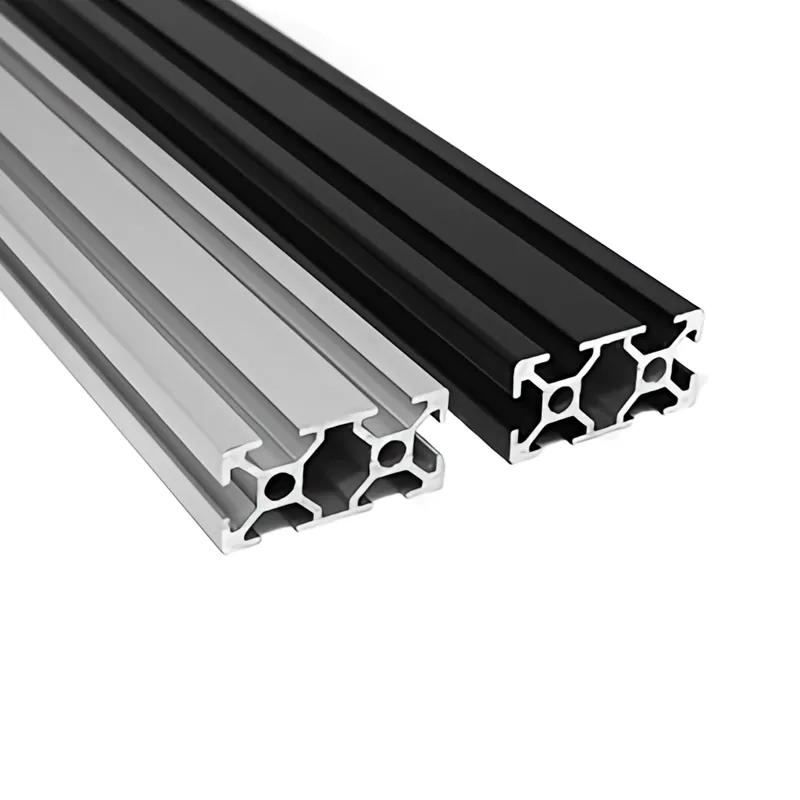
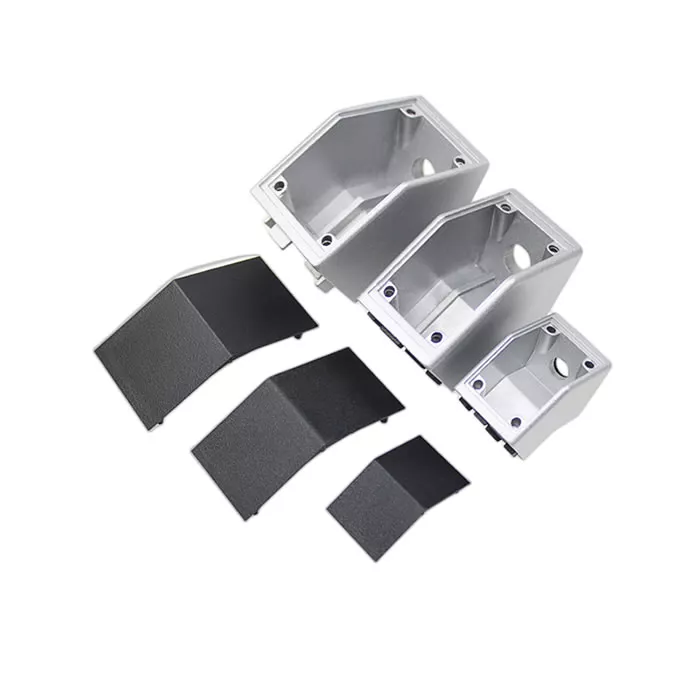
Choosing Between Extruded and Cast Aluminum
Aluminum's versatility makes it a popular choice for many manufacturing applications. Two common methods for shaping aluminum are extrusion and casting. This guide explores the key differences to help you decide which is best for your project.
Extruded Aluminum
Extrusion involves forcing heated aluminum billets through a shaped die under high pressure (up to 100,000 psi). This creates long, continuous lengths with consistent cross-sections like tubes, angles, and beams.
Benefits of Extruded Aluminum:
Economical: Especially for complex shapes with tight tolerances.
Strong and Lightweight: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
Wide Variety of Shapes: Channels, hinges, flanges, and more.
Attractive Finish: Smooth surface finish often requires minimal additional treatment.
Cast Aluminum
Casting involves pouring molten aluminum alloy into a mold. This process allows for more complex shapes and larger parts compared to extrusion. There are several casting methods, including sand casting, die casting, and investment casting.
Benefits of Cast Aluminum:
Complex Shapes: Ideal for intricate designs and near-net-shape production.
Dimensional Accuracy: Castings can achieve high tolerances.
High-Temperature Applications: Can withstand extreme operating temperatures.
Key Differences
Shape Complexity: Extrusion is limited to consistent cross-sections, while casting offers more flexibility for intricate shapes.
Size: Extruded shapes are limited by the billet size. Castings can be larger and have more varied dimensions.
Strength: Extruded aluminum tends to be stronger due to its uniform grain structure.
Surface Finish: Extruded aluminum generally has a smoother finish, while cast aluminum may require machining.
Production Cost: Extrusion is often cheaper for shorter runs, while casting might be more cost-effective for high-volume production.
Choosing the Right Method
For complex shapes, near-net-shape parts, or high-volume production, cast aluminum might be the better option.
If you need long lengths with consistent cross-sections, tight tolerances, a smooth finish, and a strong, lightweight material, extruded aluminum is a good choice.
For lower volume projects, extrusion may be more economical.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each process, you can select the most suitable method for your aluminum manufacturing needs.
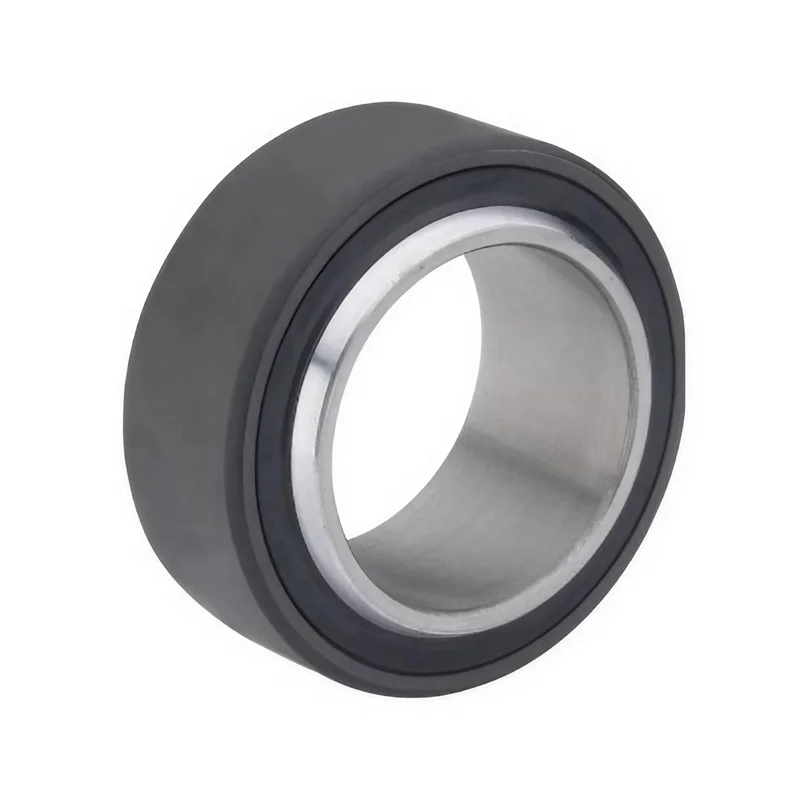
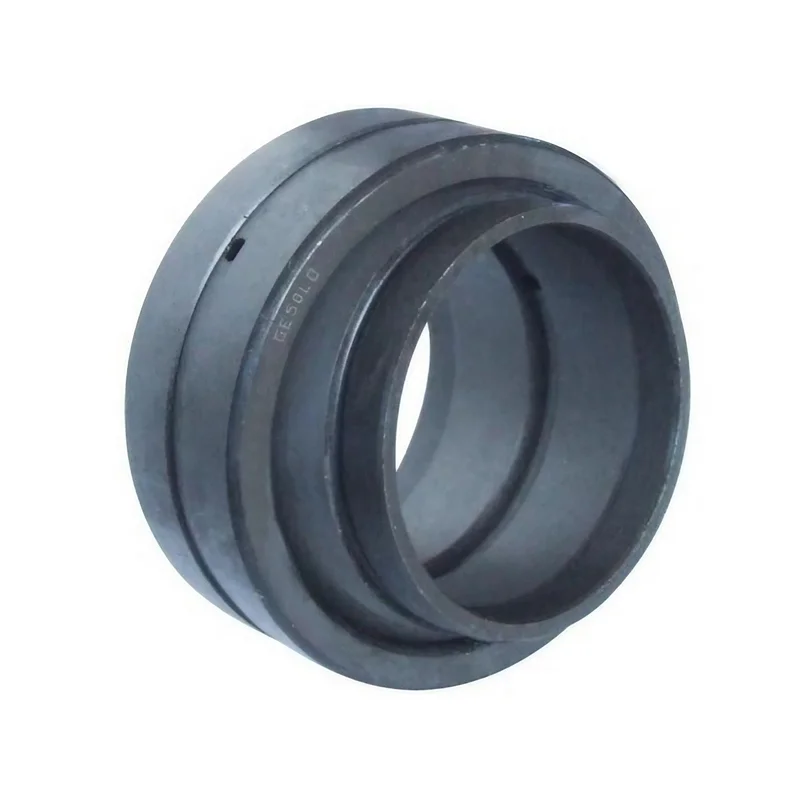
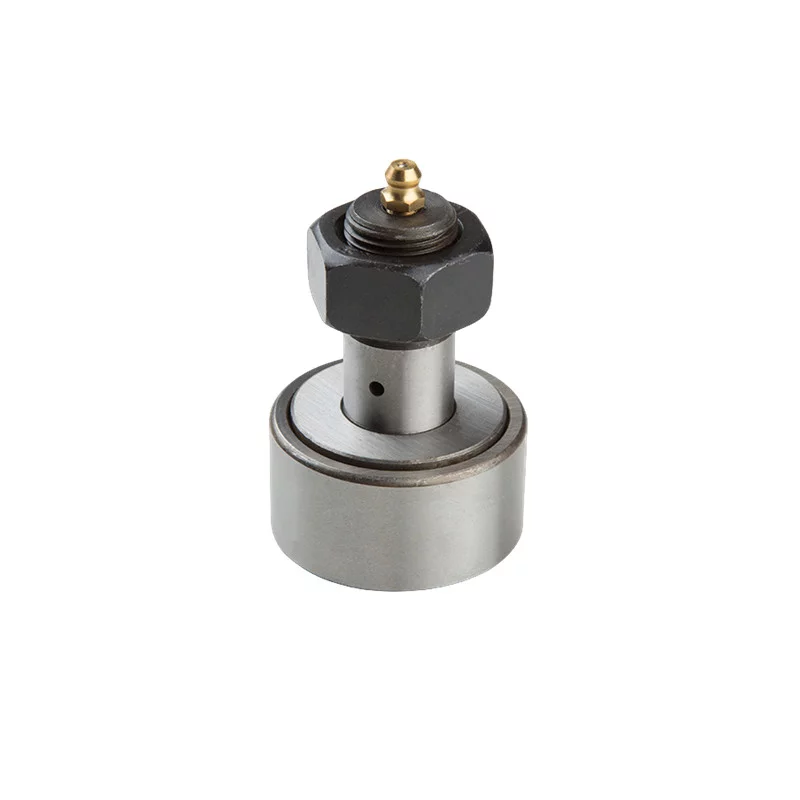 How to avoid roller bearing failures
How to avoid roller bearing failures
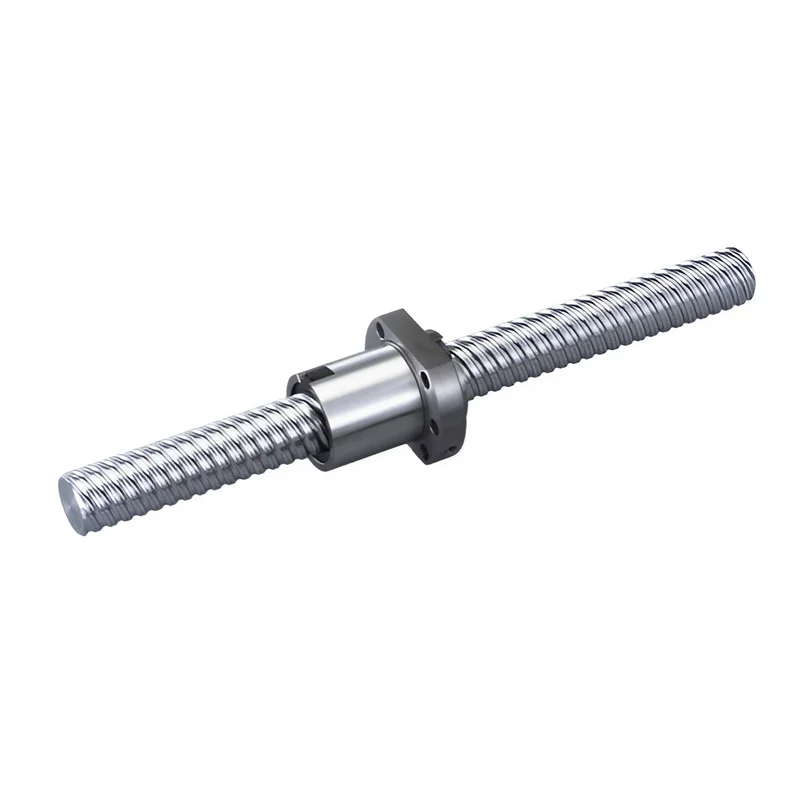
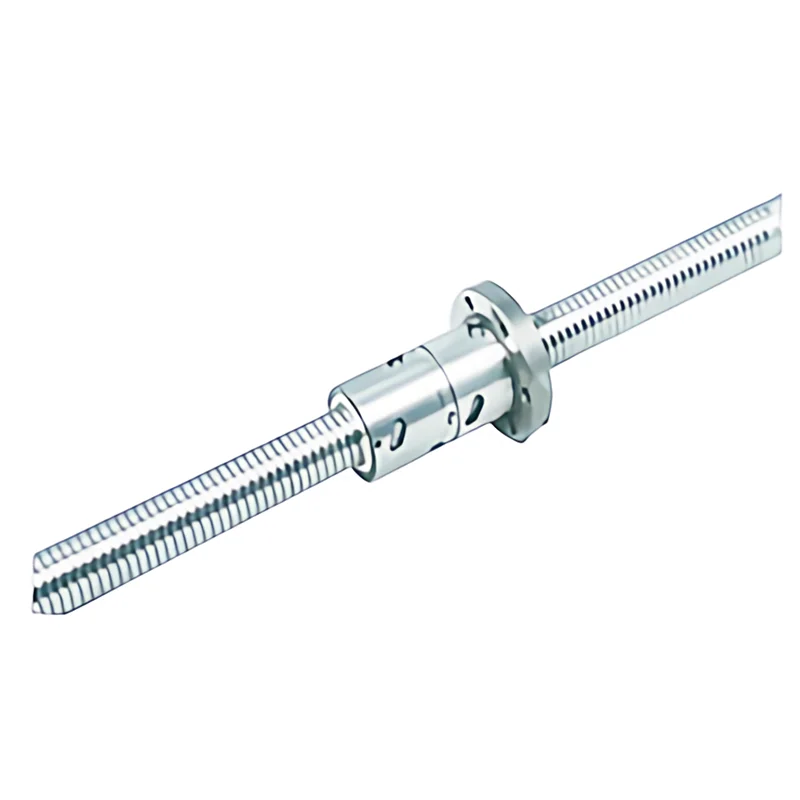
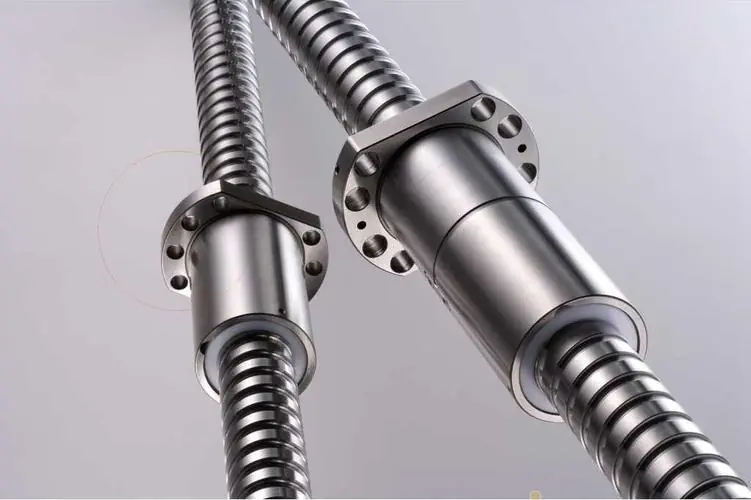 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
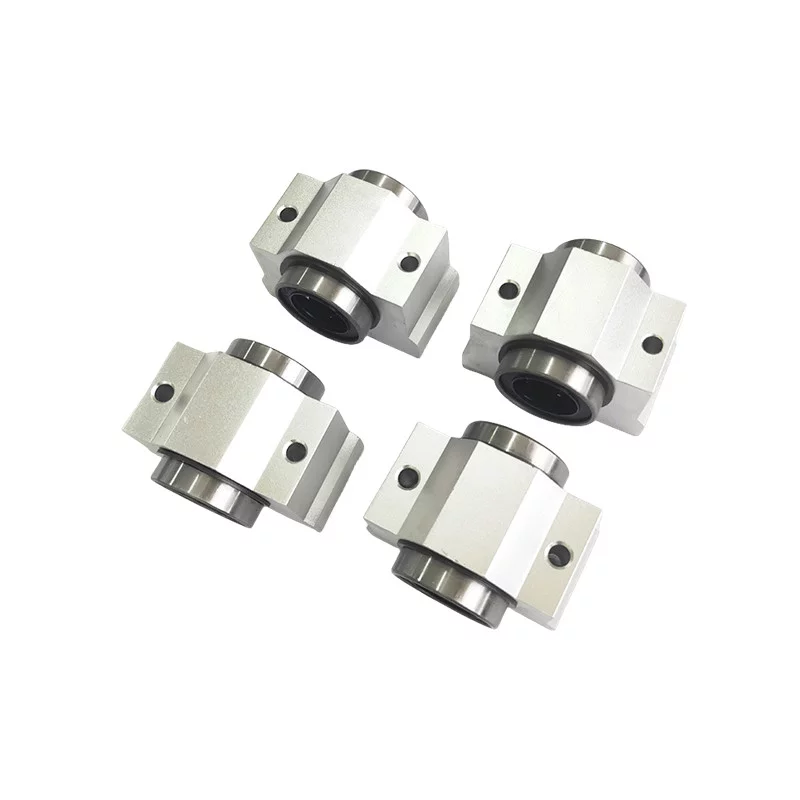
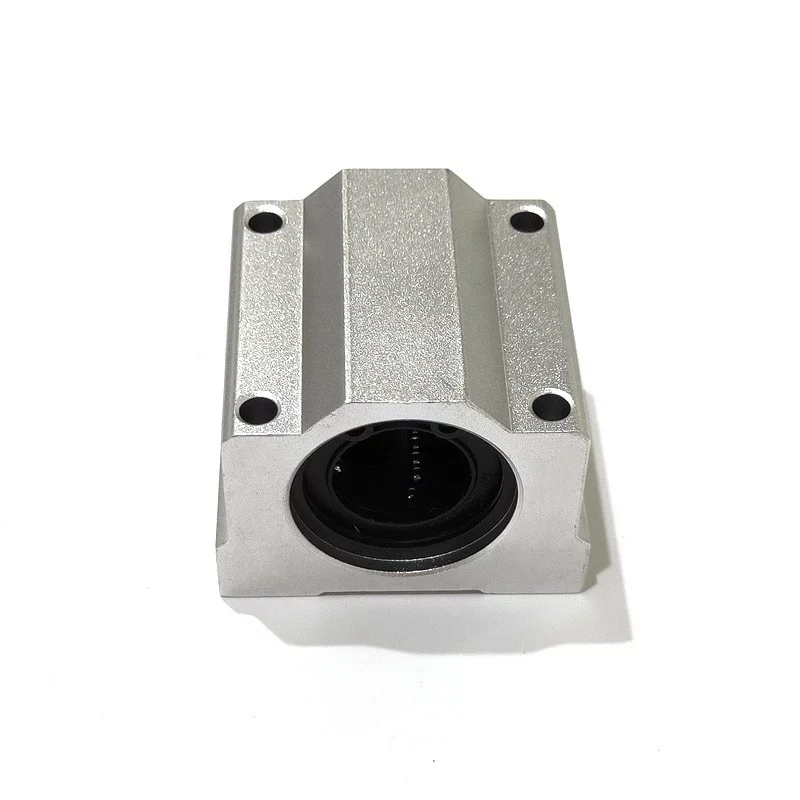 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
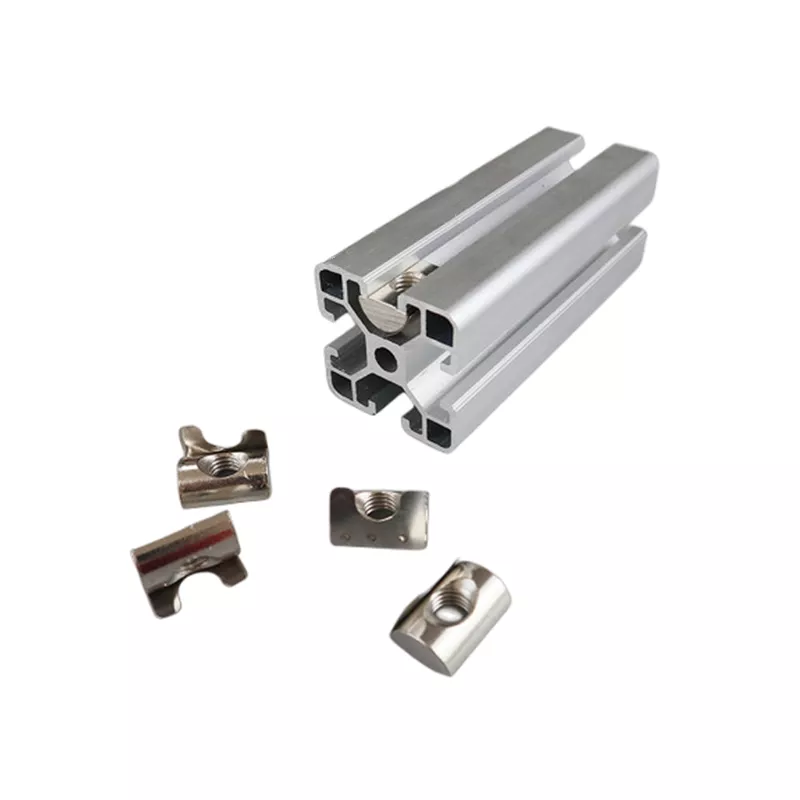
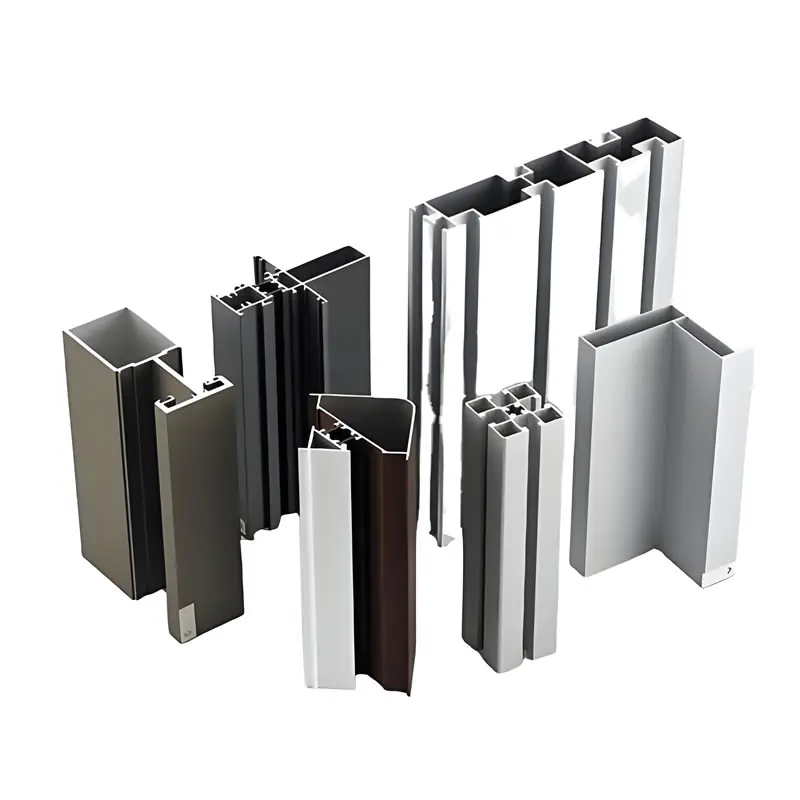 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd