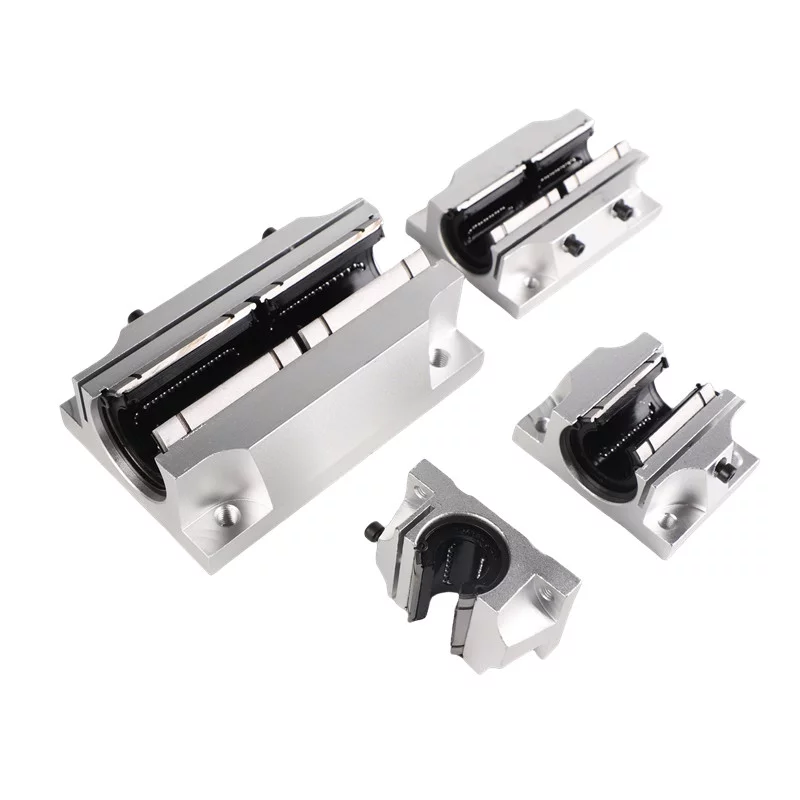
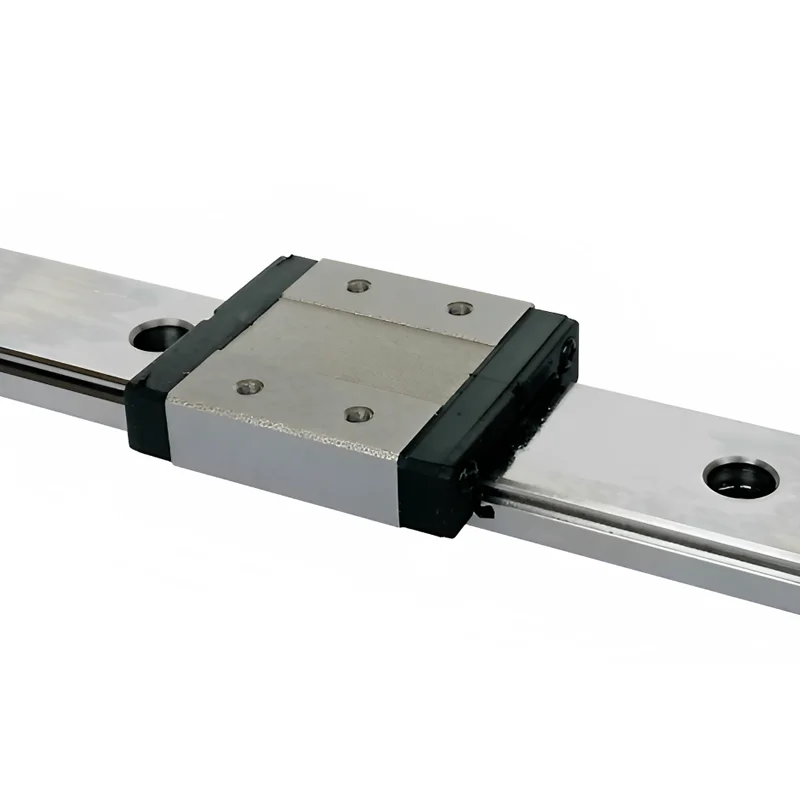
What is Linear Guide
Linear Guides are mechanical systems designed to facilitate precise linear motion along a specific path.
They consist of two main components: a rail or track and a carriage or slider.
The rail provides a stable guiding surface,
while the carriage houses rolling elements such as balls or rollers that glide along the rail's surface.
Types of Linear Guides:
1.Ball Bearing Guides
-Ball bearing guides use recirculating balls between the rail and carriage for low-friction movement.
-They offer high load capacity, smooth operation, and excellent positional accuracy.
-These guides are commonly used in machine tools, industrial automation equipment, and high-precision applications.
2.Roller Bearing Guides
-Roller bearing guides employ cylindrical rollers instead of balls for motion transmission.
-They provide higher load capacity compared to ball bearing guides but may have slightly lower positional accuracy.
-Roller bearing guides find applications in heavy-duty machinery like presses,
large-scale automation systems, and material handling equipment.
3.Plain Sliding Guides
-Plain sliding guides utilize sliding contact between the rail and carriage without rolling elements.
-They offer cost-effective solutions for lighter loads with moderate precision requirements.
-Plain sliding guides are commonly used in low-load applications such as office equipment or light-duty machinery.
Applications of Linear Guides:
1.Manufacturing Industry
-Linear guides are extensively used in CNC machines for precise tool positioning during machining operations.
-They find application in assembly lines for accurate part handling and robotic arms for controlled movement.
2.Automation Systems
-Linear Guide Systems play a vital role in various automated processes like pick-and-place operations or packaging lines.
-They ensure reliable movement control of components along predefined paths with minimal deviation.
3.Robotics
-Robots rely on linear guide systems to achieve precise movements required for tasks such as welding, painting,
material handling or surgical procedures.
-The stability provided by linear guides enhances robot performance while ensuring safety during operation.
Benefits of Linear Guide Systems:
1.High Precision: Linear guide systems offer exceptional accuracy
due to their low friction design coupled with precise manufacturing tolerances.
2.Smooth Operation: The rolling element-based design
ensures smooth gliding motion with minimal noise even at high speeds.
3.Load Capacity: Depending on the type chosen,linear guide systems
can handle varying load capacities from light-duty to heavy-duty applications.
4.Longevity & Durability: Properly maintained linear guide systems exhibit excellent durability,
ensuring prolonged service life even under demanding conditions.
 How to avoid roller bearing failures
How to avoid roller bearing failures
 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd