What are the differences between plain and rolling linear guides
Linear Guides with plain (sliding) motion
Plain bearings are the most basic type of linear guide system,
operating on the principle of sliding contact between two surfaces.
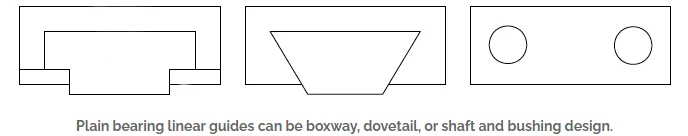
They can be constructed in various forms such as boxway,
dovetail, or shaft and bushing configurations.
Boxway bearings are known for their ability to handle high loads,
while dovetail designs offer advantages in terms of ease of machining and assembly.
On the other hand, plain bearing bushings are simple to manufacture
and install but have limitations in terms of load capacity due to their unsupported shafts,
which makes them susceptible to deflection.
Plain bearings have a high coefficient of friction,
typically 0.05 to 0.1, when compared to rolling element bearings.
But, unlike rolling elements, they can withstand shock loads
and vibrations without significant damage to the surfaces.
Plain bearings are also less sensitive to contamination,
and rarely experience catastrophic failure.
Linear guides with rolling motion
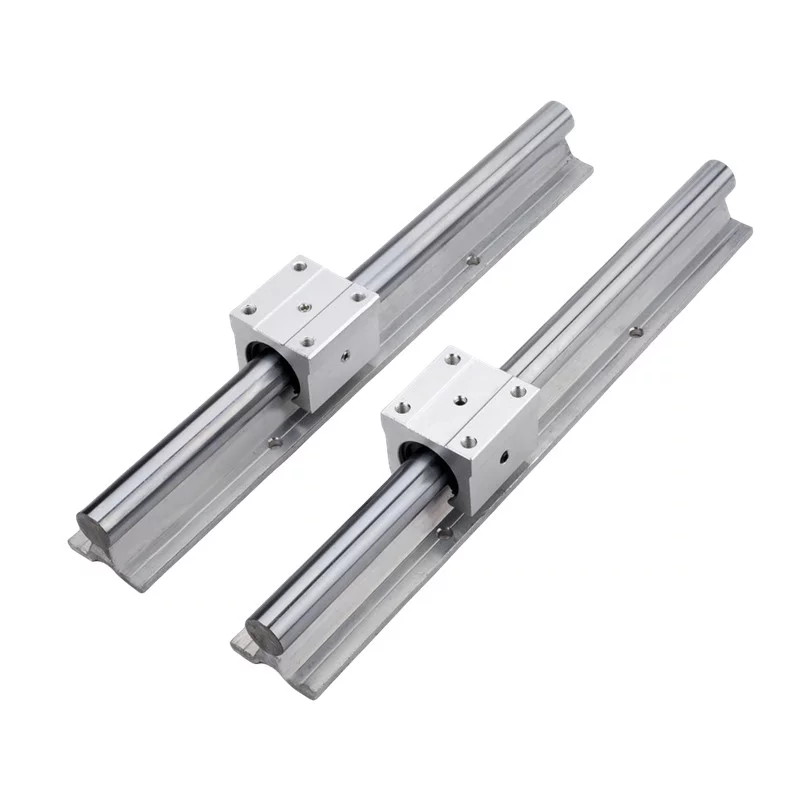
Rolling element linear guides incorporate balls or rollers between the two surfaces of the guide system.
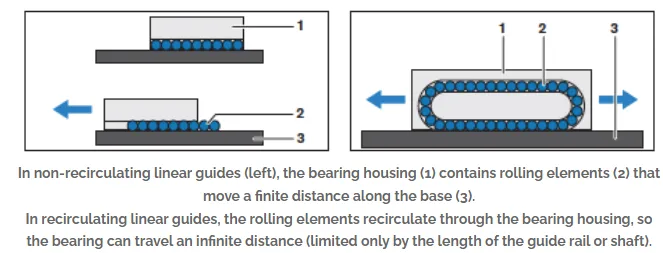
There are two main types of rolling bearings: recirculating and non-recirculating designs.
Recirculating rolling bearings, such as profiled rail guides or linear bushing/Linear Bearing guides,
enable unlimited motion along the length of the guide rail or shaft.
These designs feature rolling elements that circulate within a closed loop,
allowing smooth and continuous movement.
Non-recirculating rolling bearings, such as cam roller guides or crossed-roller slides,
have a limited stroke length determined by the size of the bearing.
These designs do not feature a closed loop for the rolling elements
and are typically used in applications where shorter strokes are sufficient.
Both recirculating and non-recirculating rolling element linear guides
offer advantages depending on specific application requirements.
Recirculating designs provide flexibility in terms of stroke length
and can handle longer travel distances with high precision.
Non-recirculating designs are often more compact
and suitable for applications with shorter stroke requirements.
Overall, rolling element linear guides enhance motion control by reducing friction,
increasing load capacity, and improving positional accuracy compared to plain bearing systems.
 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
 Enhance Industrial Efficiency with Premium Cylinder End Bearings from SAIVS
Enhance Industrial Efficiency with Premium Cylinder End Bearings from SAIVS