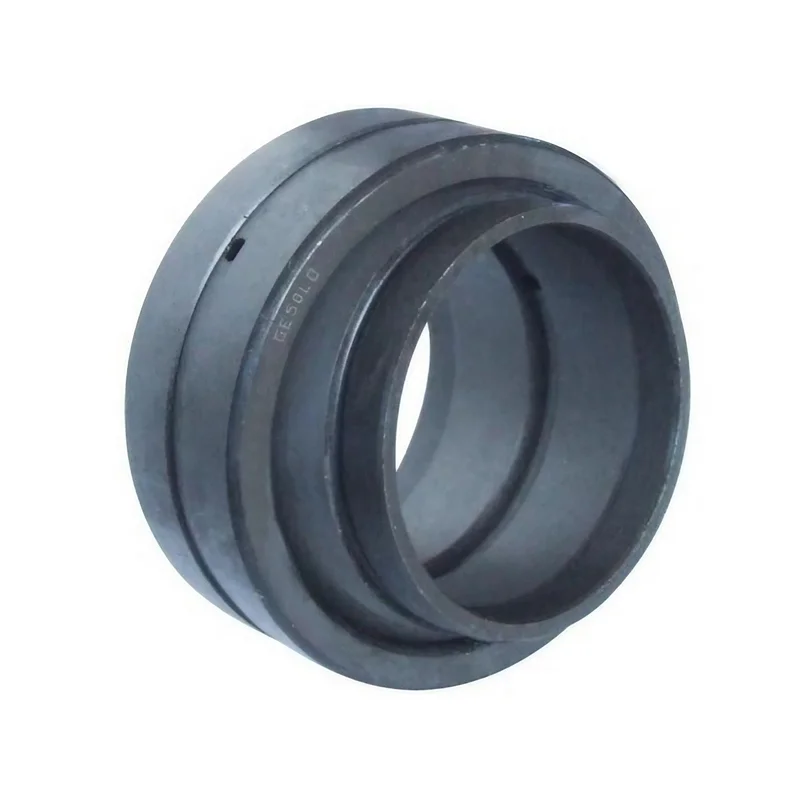
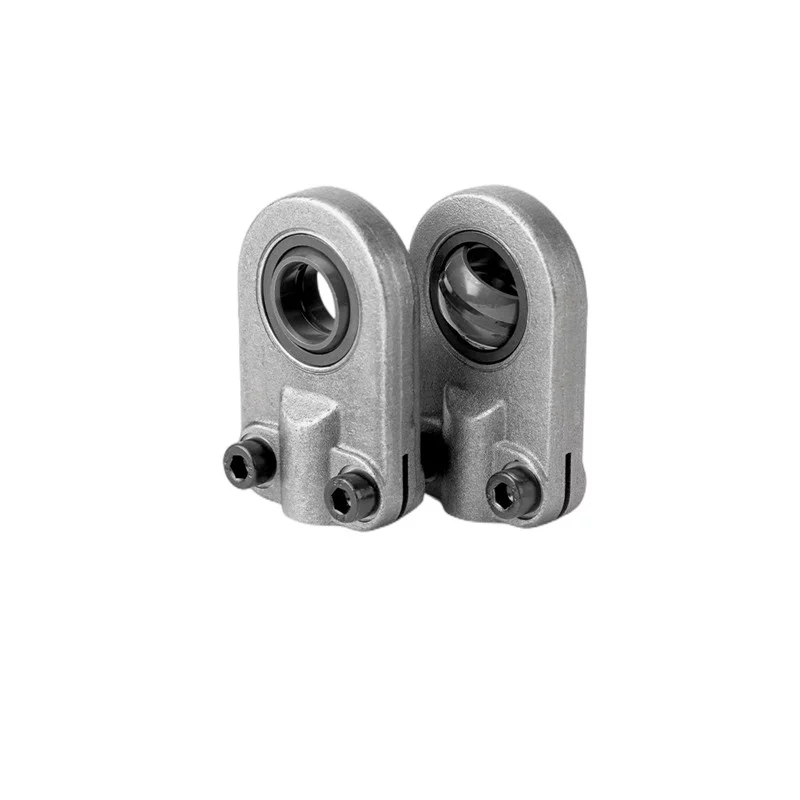
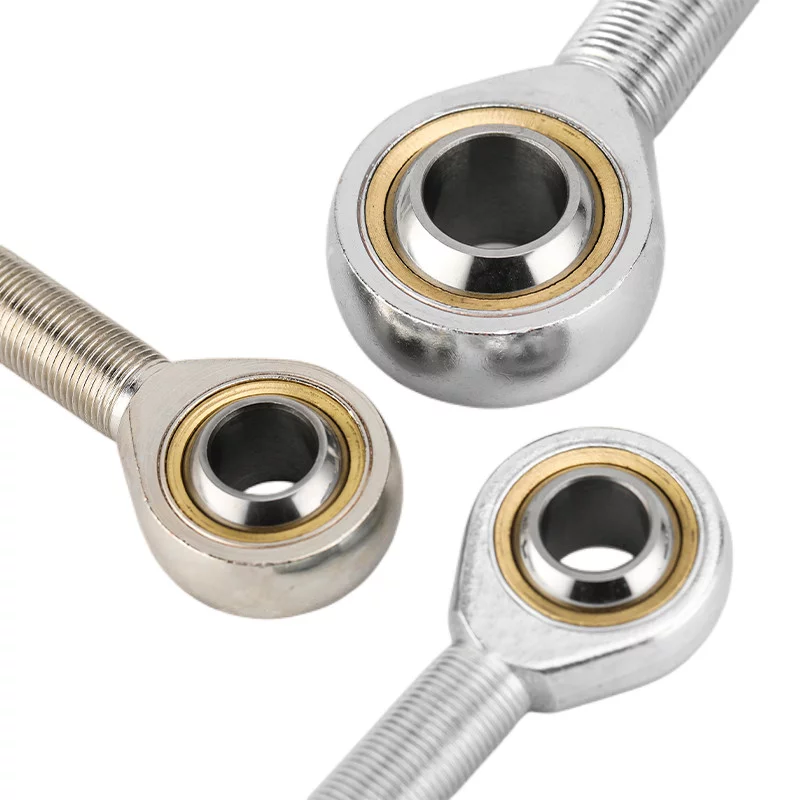
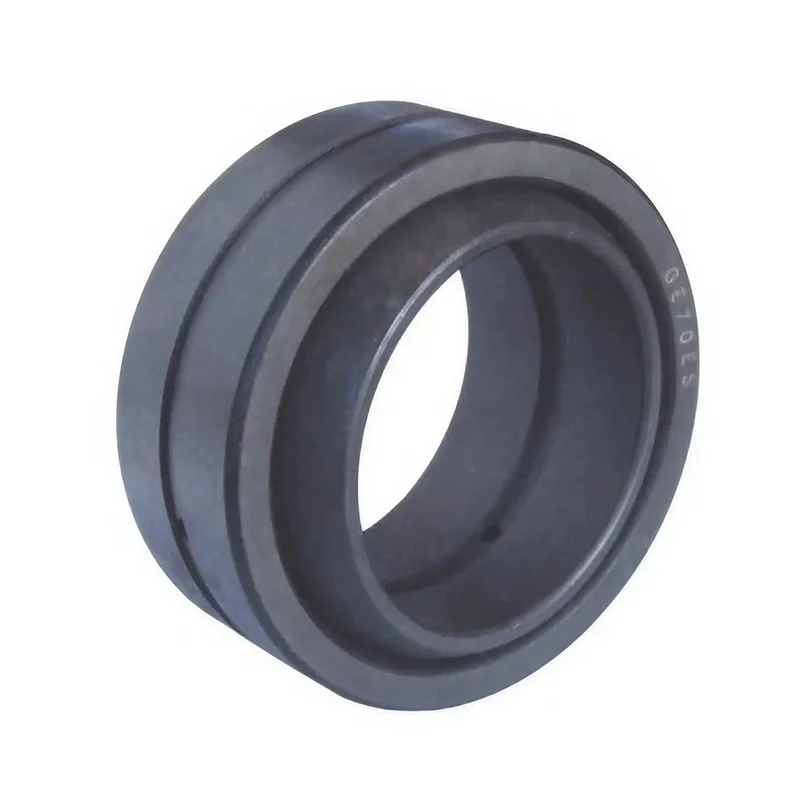
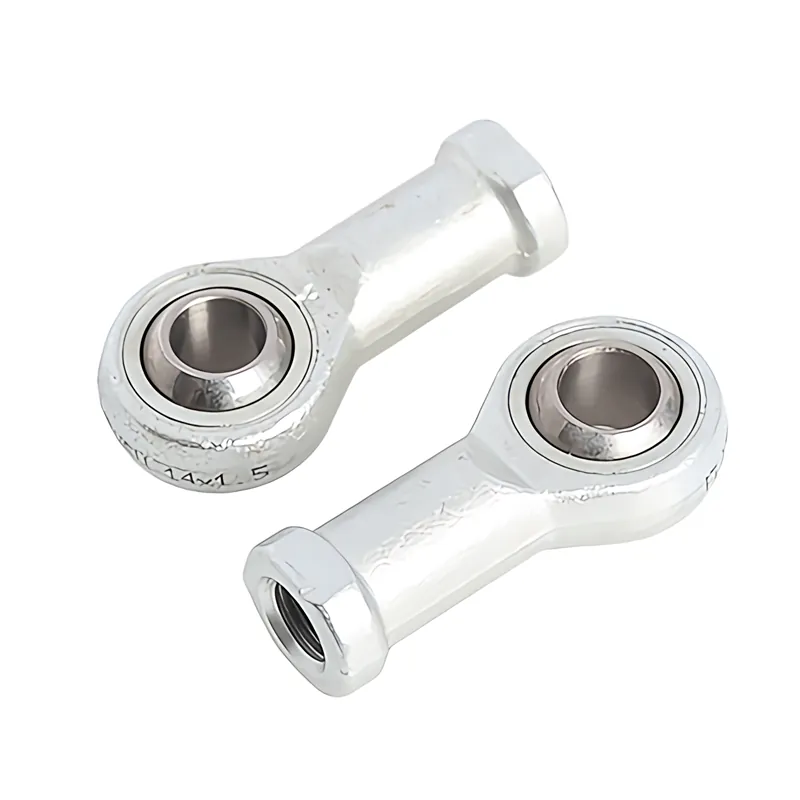
What is Hydraulic Joint Bearings
Joint bearings are a type of spherical sliding bearings,
with sliding contact surfaces consisting of an inner spherical surface and an outer spherical surface.
They can rotate and swing at any angle during movement.
They are made using various special processing methods
such as surface phosphating, blasting, pad insertion, and spraying.
Joint bearings have the characteristics of high load capacity, impact resistance, corrosion resistance,
wear resistance, self aligning, and good lubrication.
The structure of joint bearings is simpler than that of rolling bearings, mainly consisting of an inner
ring with an outer spherical surface and an outer ring with an inner spherical surface.
Joint bearings are generally used for low speed swing motion (i.e. angular motion).
Due to the spherical sliding surface, they can also perform tilting motion
(i.e. centering motion) within a certain angle range.
They can still work normally when the support shaft and the shaft shell hole are not concentric.
Joint bearings are widely used in various mechanical equipment, such as automobiles, agricultural machinery,
engineering machinery, aerospace equipment, railway vehicles, ships, and other fields.
Due to its special self-aligning ability, joint bearings can reduce the adverse effects caused by machine deformation,
improve the operating accuracy and reliability of the machine,
and also reduce the wear between the bearings and the frame, extending the service life of the bearings.
In addition, joint bearings can also operate in harsh environments or under insufficient lubrication conditions,
making them known as the "universal oil in the field of machinery".
In short, joint bearings are a widely used, reliable, and convenient mechanical component,
which is of great significance for modern industrial production.
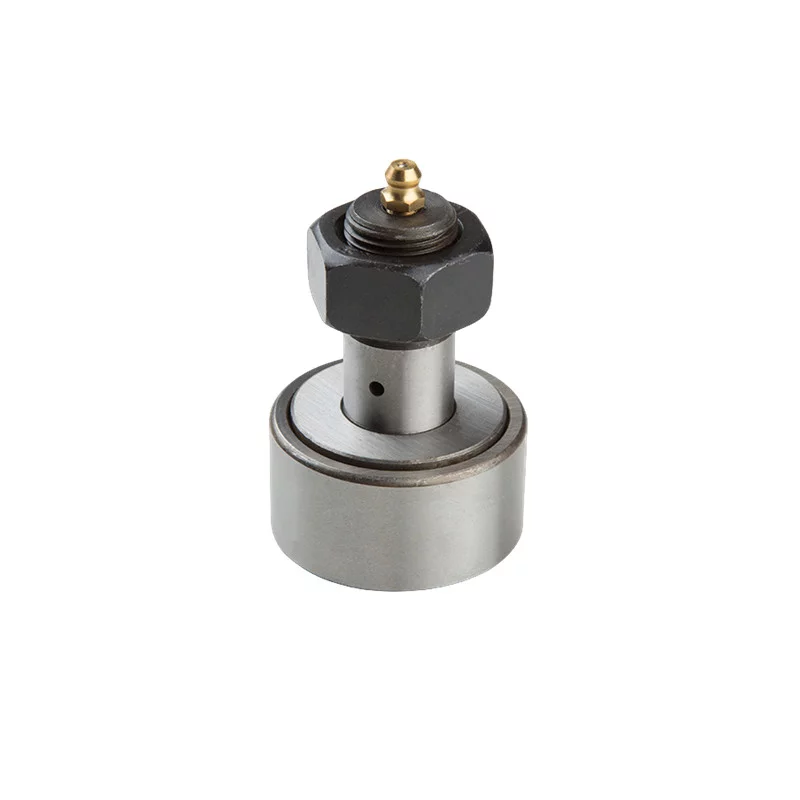 How to avoid roller bearing failures
How to avoid roller bearing failures
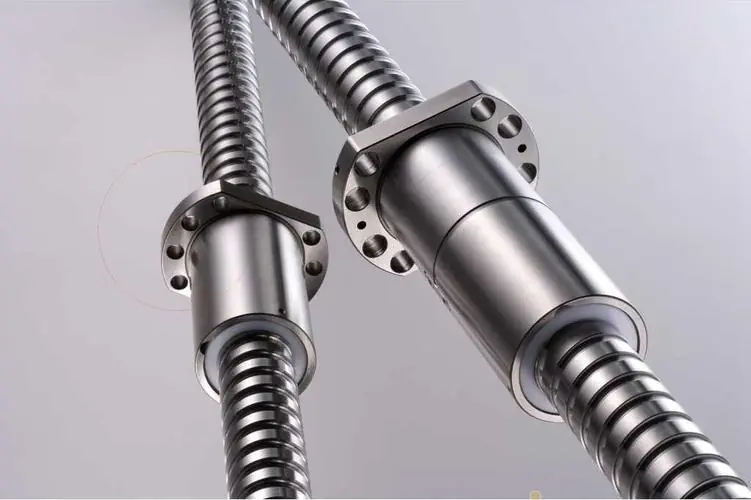 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
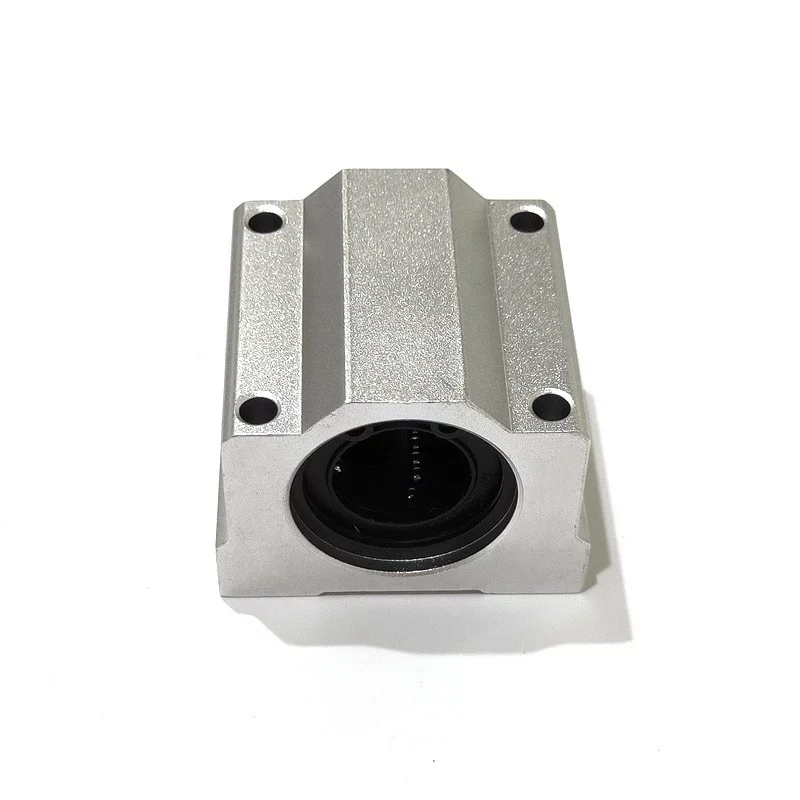 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
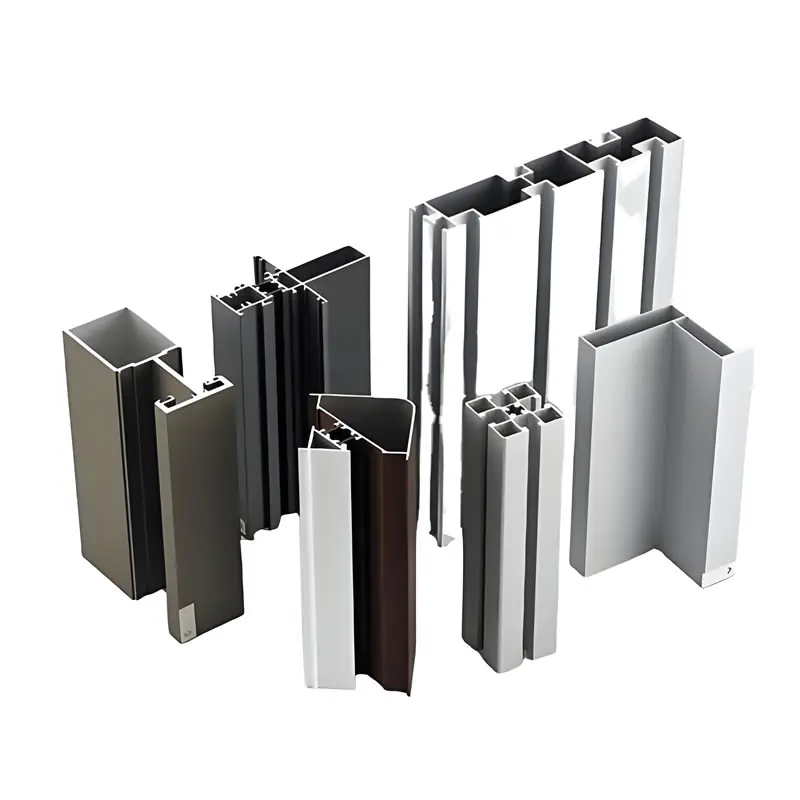 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd