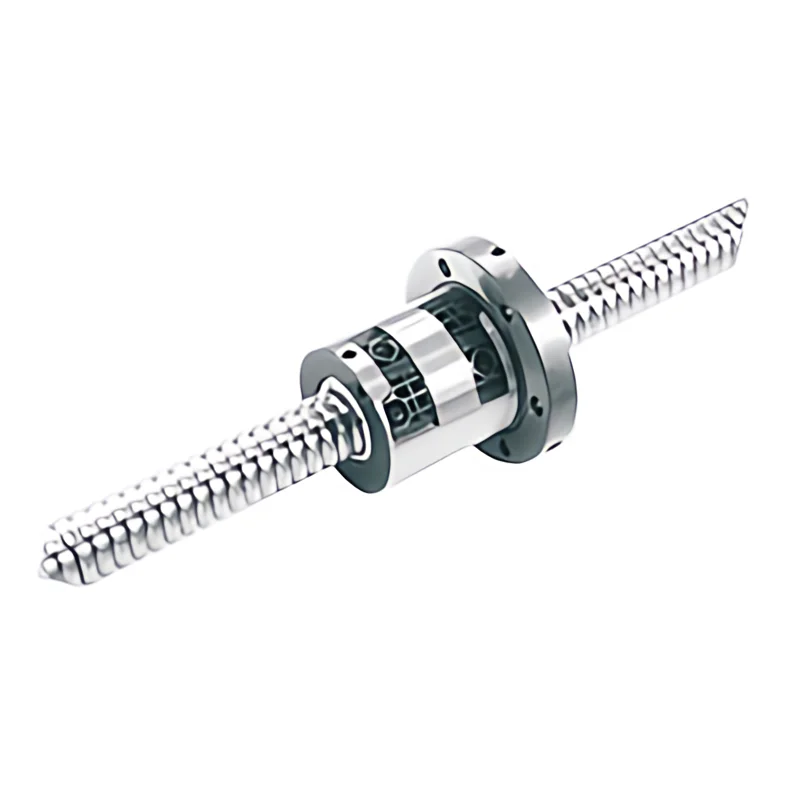
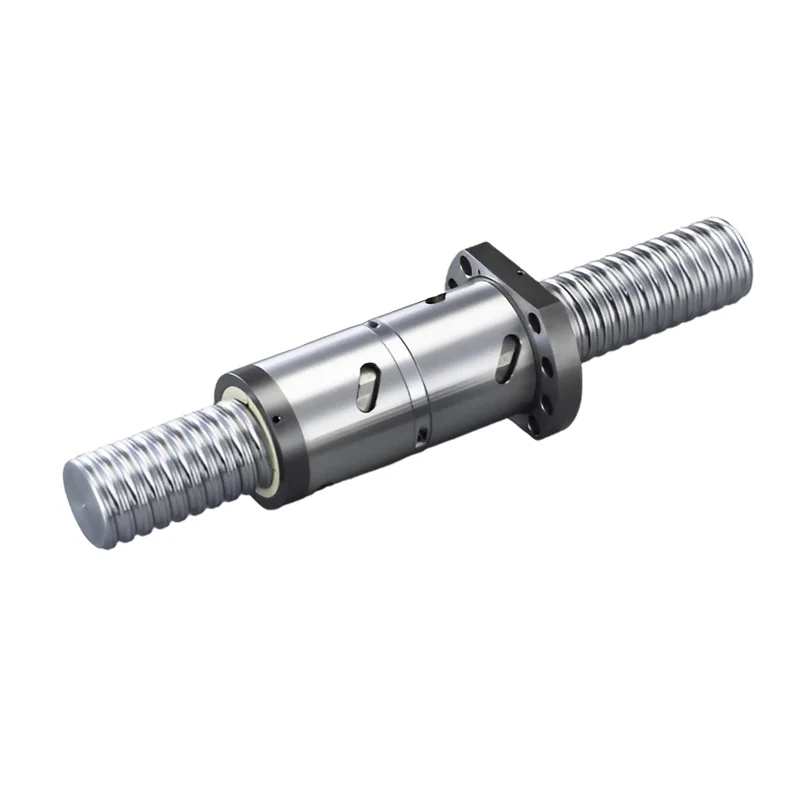
Types of Ball Screws
Ball Screws are an essential component in numerous industrial and scientific applications that require precise and smooth linear motion.
They are made in various configurations, including miniature, rolled, ground, and precision, to meet the diverse range of requirements.
To meet the various requirements of their applications, balls crews are available in multiple configurations,
such as miniature, rolled, ground, and precision.
Miniature ball screws are popular for use in lasers, gauge measurement devices, semiconductors,
medical instruments, and other small devices that require smooth and precise linear motion.
Rolled ball screws, or roll ball screws, are named as such because, beginning as blank metal workpieces,
they are formed through cold screw rolling.
These cold rolled ball screws offer the advantage of a positional precision of several thousandths of an inch per foot.
Rolled screw threads are created through cold work deformation.
The grooves are formed by passing the uncut blank shaft through rotating tool dies;
the substantial plastic deformation of the blank produces a high-strength screw shaft.
Compared to ground screws, rolled screws are more affordable and simpler to manufacture.
Ground ball screws, which boast extremely high levels of precision, are made in three steps:
machining to gross shape, case hardening, and grinding.
This grinding takes place on rapidly spinning machines that are coated with abrasive materials.
This treatment bestows upon the finished ground screws the ability to withstand temperatures
that would normally distort their shape and mar their efficiency.
Ground ball screws are best for applications that require not only high precision, but high stiffness.
In conclusion, the choice of ball screw configuration depends on the specific application requirements,
such as precision, stiffness, durability, and affordability.
Whether it is miniature, rolled, or ground, a ball screw is a crucial element that enables highly accurate and
repeatable linear motion in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, medical, semiconductor, and automation.
 How to avoid roller bearing failures
How to avoid roller bearing failures
 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd