The Indispensable Role of Ball Screws in Humanoid Robots
The Unsung Heroes of Humanoid Motion: Ball Screws
Humanoid robots, with their ability to mimic human movements, are rapidly transforming industries from manufacturing to healthcare. But behind their graceful gestures and precise actions lies a critical component often overlooked: the ball screw. This seemingly simple device plays a pivotal role in enabling these robots to move with accuracy and power.

What is a Ball Screw?
A ball screw is a mechanical linear actuator that converts rotational motion into linear motion with minimal friction. It consists of a screw shaft with helical grooves, a nut, and balls that roll between the screw and the nut. This design allows for smooth and efficient movement, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and high load capacity.
Why are Ball Screws Essential for Humanoid Robots?
Precise Movement: Humanoid robots need to perform intricate movements, from walking and grasping to manipulating objects. Ball screws provide the precise linear motion required for these tasks, ensuring that the robot's actions are accurate and repeatable.
High Load Capacity: Humanoid robots often need to lift heavy objects or withstand external forces. Ball screws are designed to handle high loads, making them suitable for robots that require strength and stability.
Efficiency: The low friction design of ball screws translates to high efficiency, meaning that minimal energy is lost during motion. This is crucial for humanoid robots that need to conserve power and operate for extended periods.
Compact Design: Ball screws are relatively compact, allowing them to be integrated into the limited space available in humanoid robots. This is particularly important for robots with complex designs and multiple joints.
Applications of Ball Screws in Humanoid Robots
Ball screws are used in various joints and limbs of humanoid robots, including:
Legs: Ball screws enable the precise movement of the legs, allowing the robot to walk, run, and climb stairs.
Arms: Ball screws facilitate the accurate movement of the arms, enabling the robot to grasp objects, perform tasks, and interact with the environment.
Neck: Ball screws allow for the smooth rotation and tilting of the head, enabling the robot to scan its surroundings and communicate effectively.
The Future of Ball Screws in Humanoid Robots
As humanoid robots become more sophisticated, the demands on their components, including ball screws, will continue to increase. Future developments in ball screw technology are likely to focus on:
Miniaturization: Making ball screws smaller and lighter to fit into even more compact robot designs.
Increased Precision: Improving the accuracy and repeatability of ball screws to enable even more intricate movements.
Enhanced Durability: Developing ball screws that can withstand harsh environments and operate for longer periods without maintenance.
Conclusion
Ball screws are indispensable components in humanoid robots, enabling them to move with precision, power, and efficiency.
As humanoid robot technology advances, ball screws will continue to play a crucial role in bringing these remarkable machines to life.
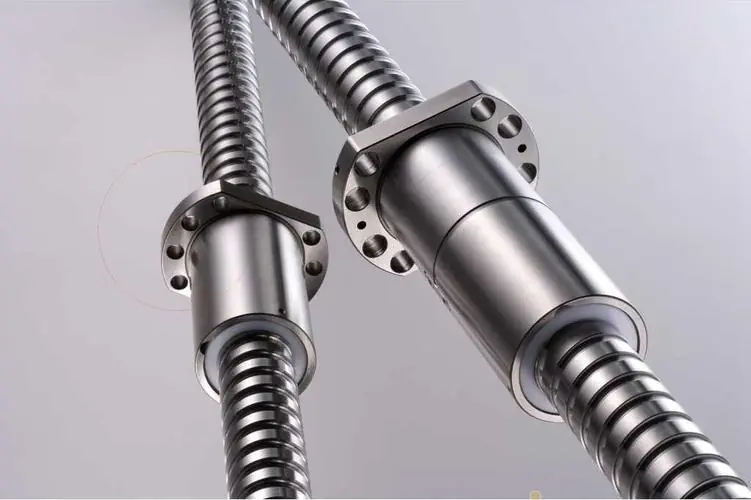 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
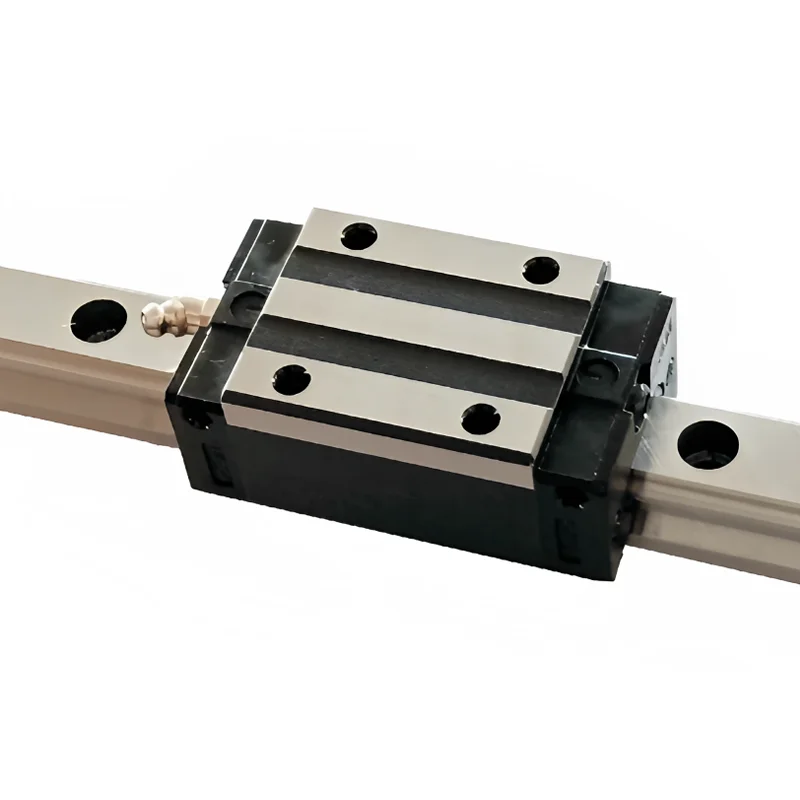
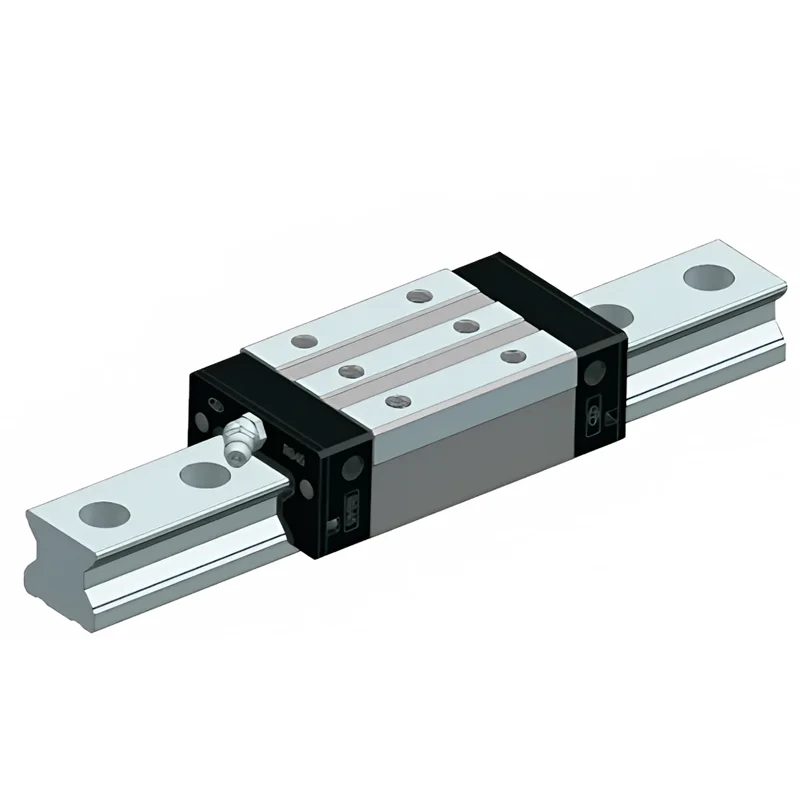
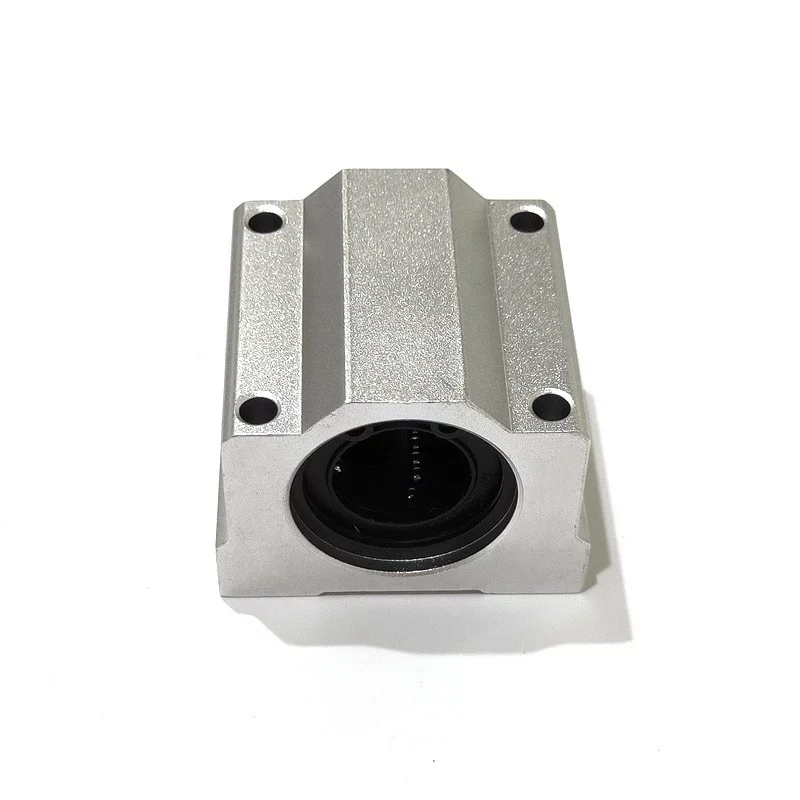 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
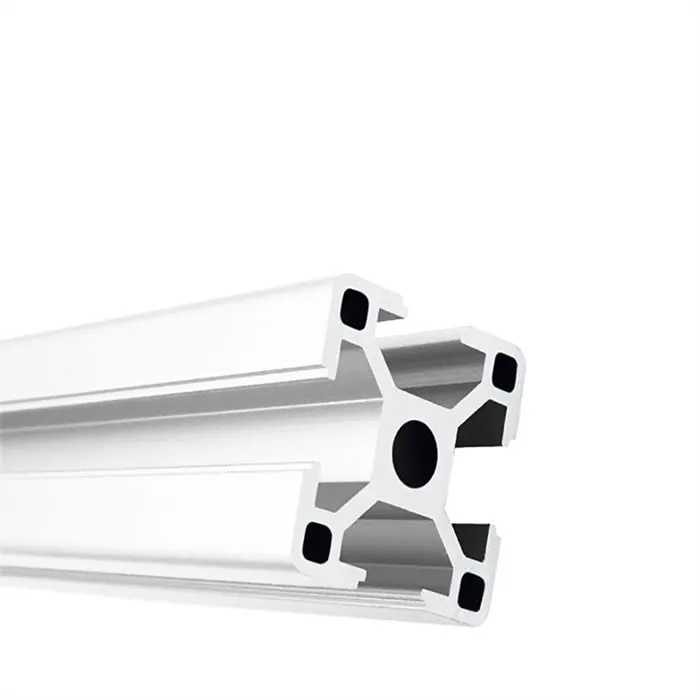
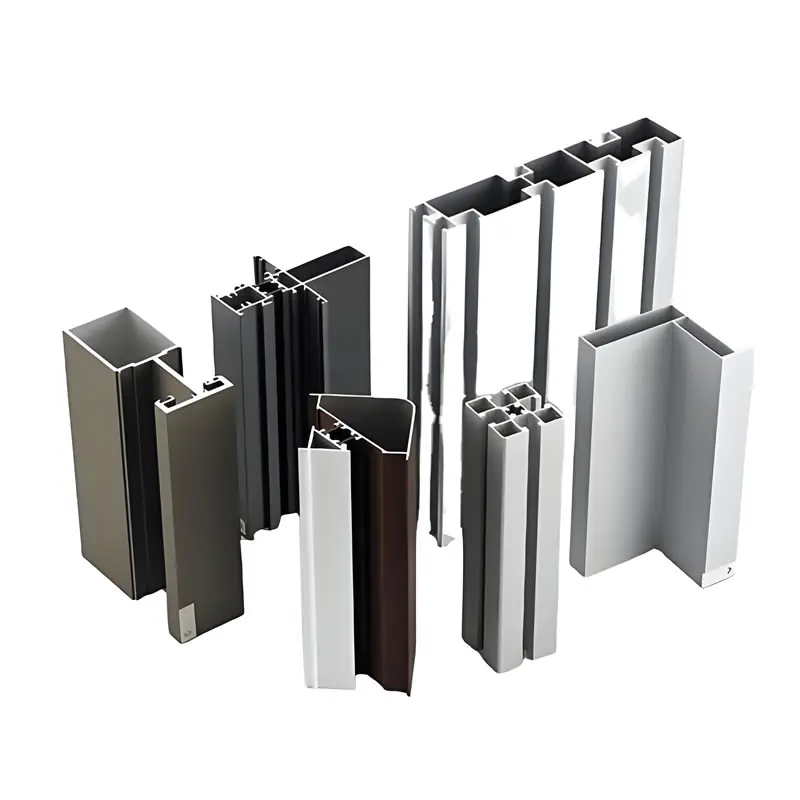 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
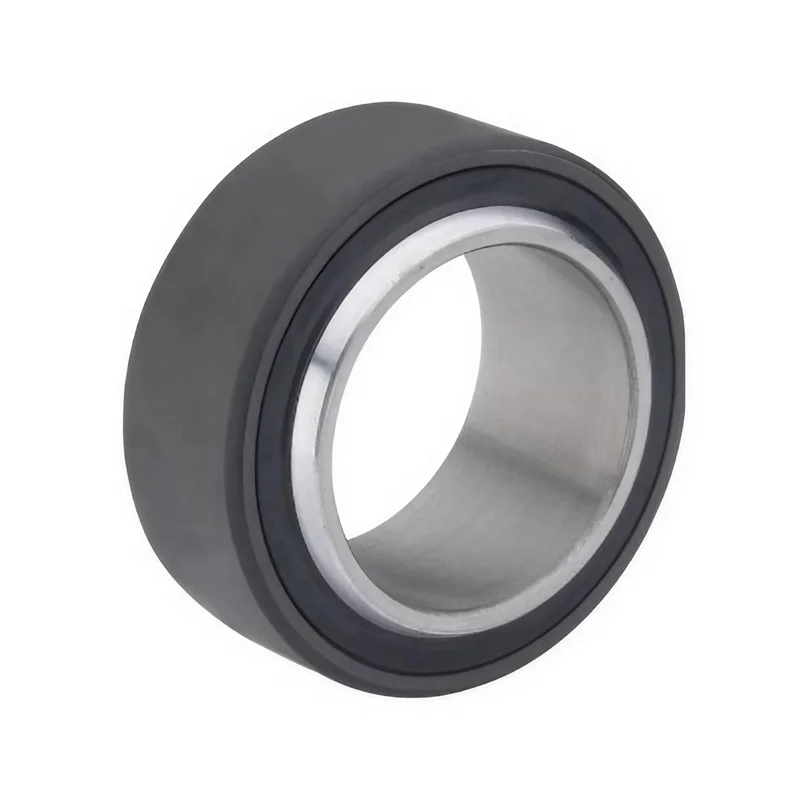
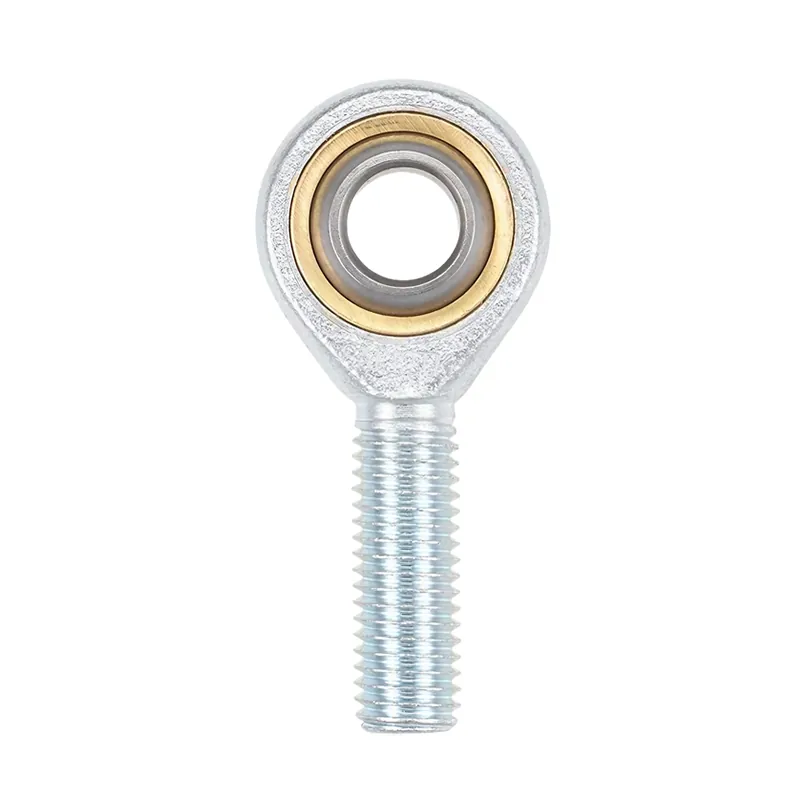 Enhance Industrial Efficiency with Premium Cylinder End Bearings from SAIVS
Enhance Industrial Efficiency with Premium Cylinder End Bearings from SAIVS