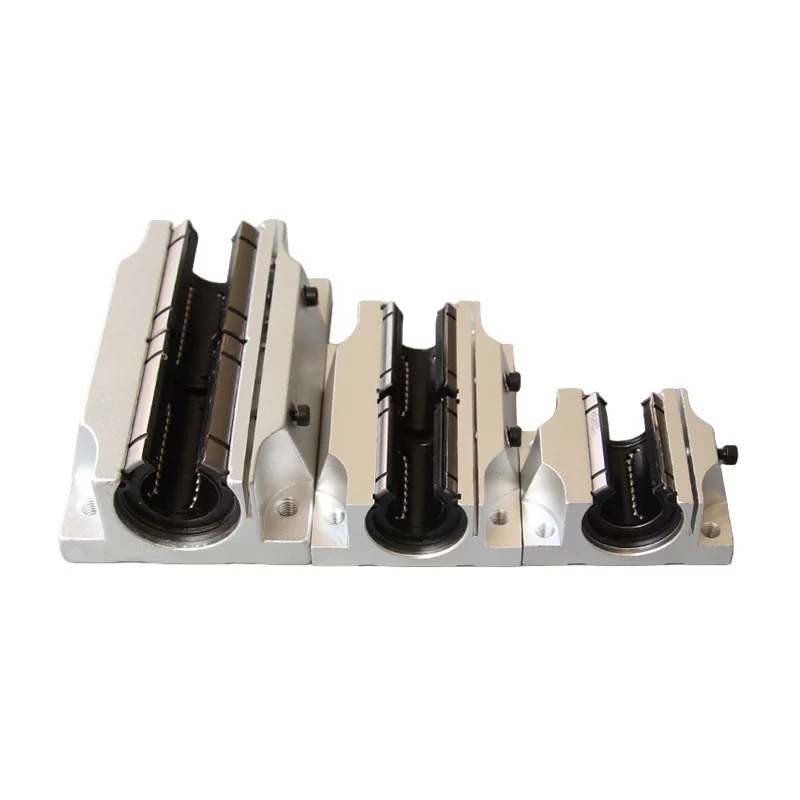
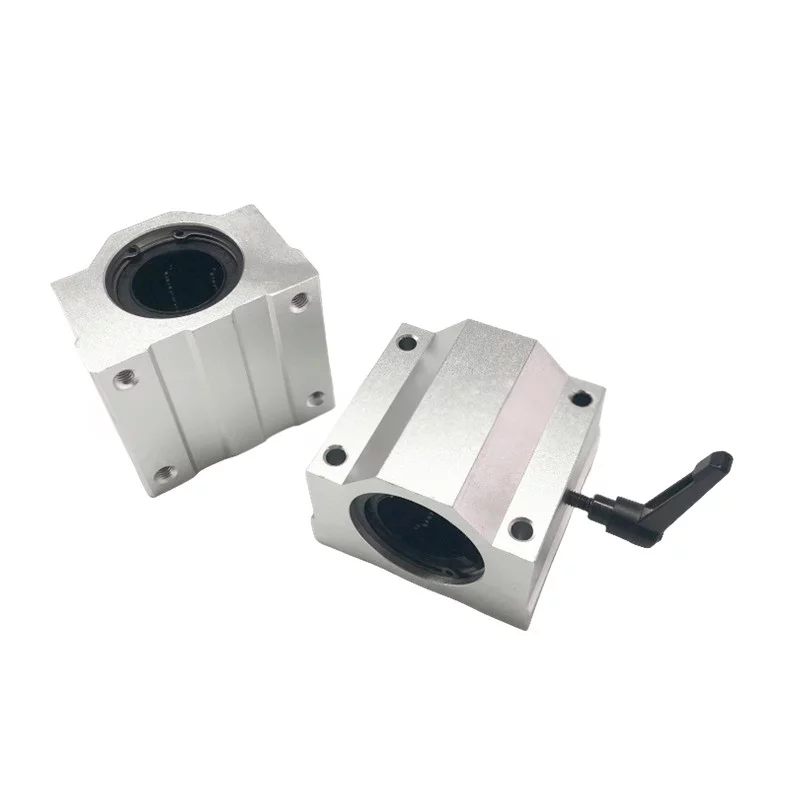
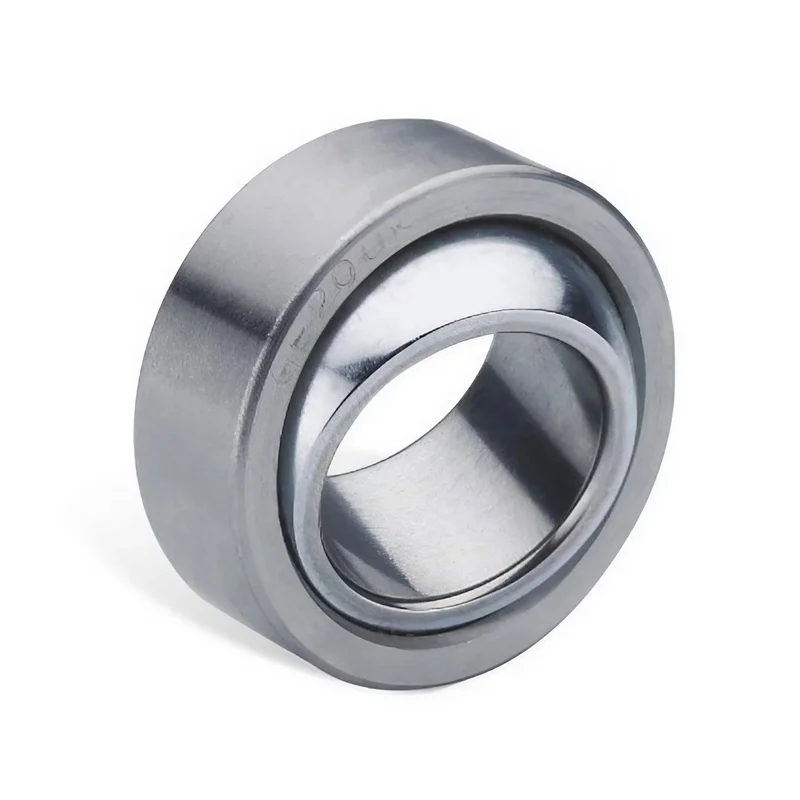
Schematic diagram of linear bearing structure
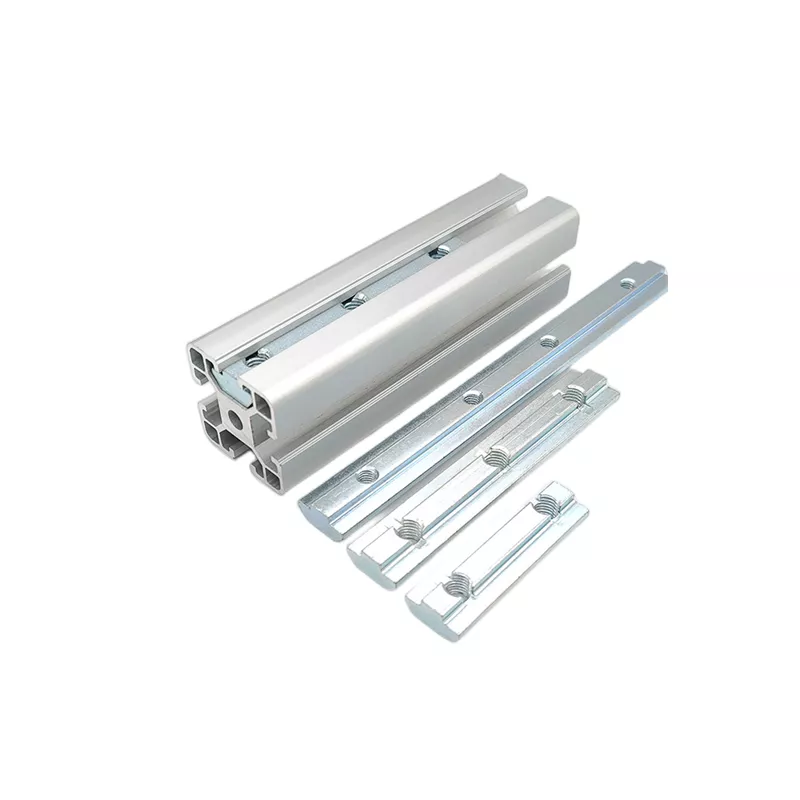
Base: The base is the foundation of the Linear Bearing structure.
It's typically a rigid frame or platform that provides stability and support.
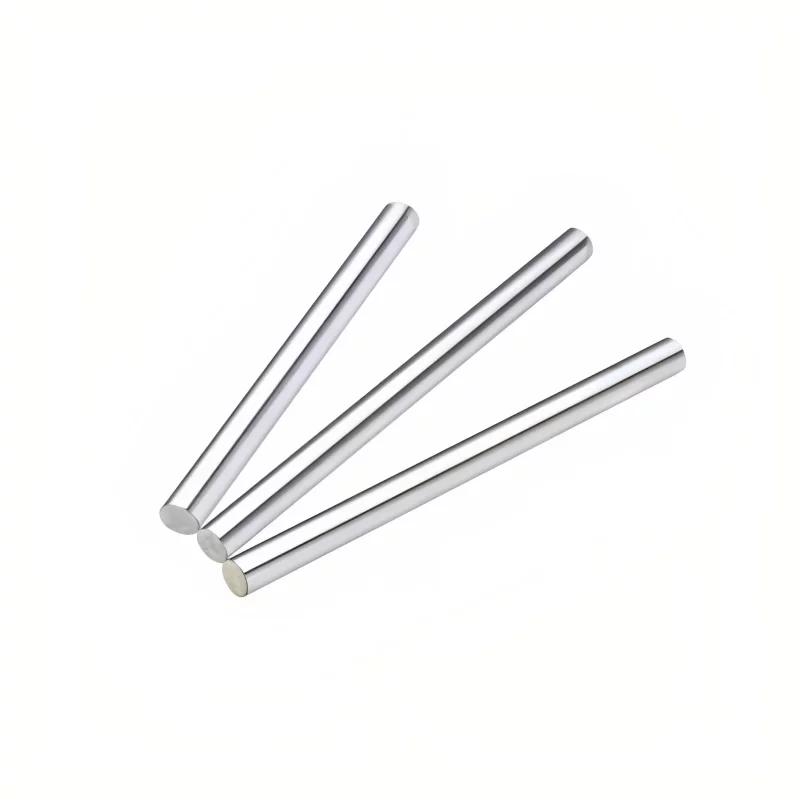
Rail: The rail is a long, straight component attached to the base.
It serves as the guiding track for the linear motion.
It's often made of hardened steel or other durable materials.
The rail can have different profiles, such as cylindrical or square,
depending on the specific type of linear bearing.
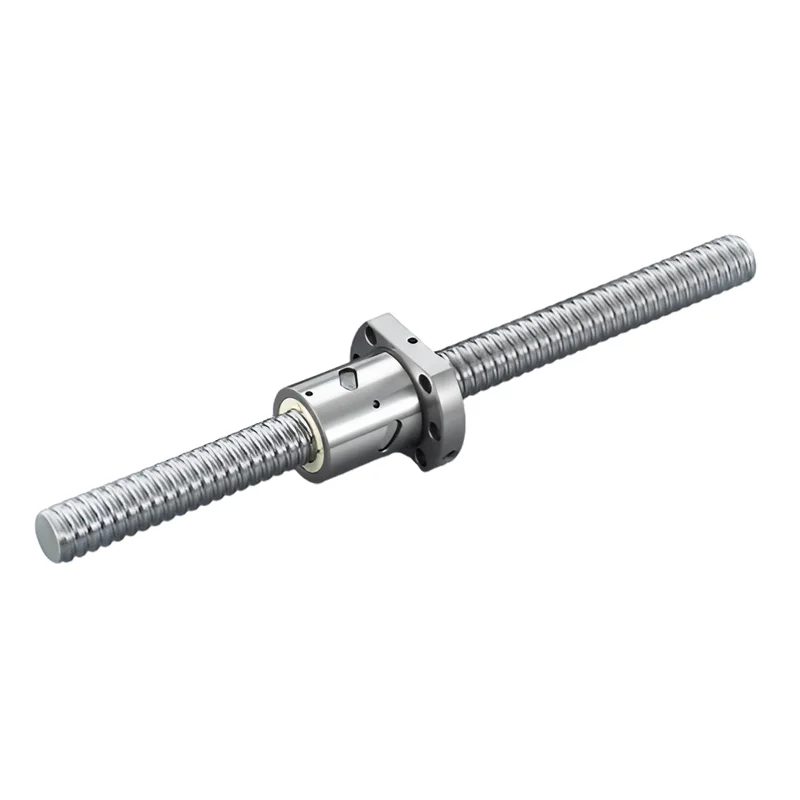
Slider/Carriage: The slider or carriage is the moving component that rides along the rail.
It contains the load (object or equipment) that needs to be moved linearly.
The slider is equipped with bearings that allow it to move smoothly along the rail.
Bearings: Bearings are crucial elements in a linear bearing structure.
They are designed to reduce friction between the rail and the slider,
ensuring smooth and precise movement.
There are various types of linear bearings,
including ball bearings, roller bearings, and plain bearings.
Seals/Covers: Linear bearing structures may have seals or covers to protect
the internal components (such as bearings) from dust, dirt, and contaminants.
This helps extend the lifespan of the bearings and maintains their performance.
Mounting Brackets: These are used to attach the linear
bearing structure to other parts of a machine or system.
They provide stability and proper alignment.
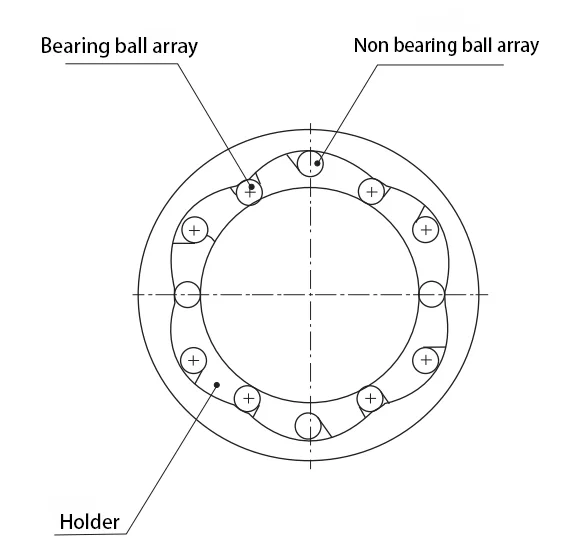
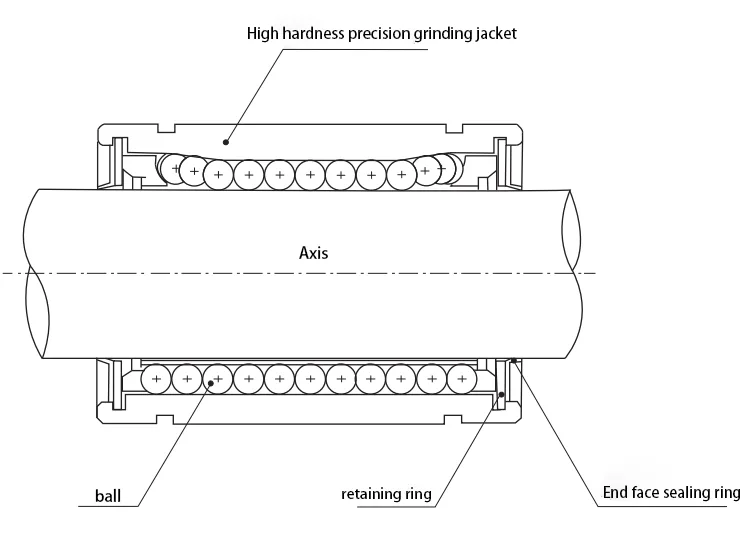
In conclusion, a linear bearing structure consists of several key components working together to facilitate smooth and precise linear motion. The base provides stability and support, while the rail serves as the guiding track. The slider or carriage carries the load and moves along the rail, enabled by bearings that minimize friction. Seals or covers protect internal components from contaminants, prolonging their lifespan. Mounting brackets ensure stability and alignment within the overall system. Together, these components form a reliable and efficient solution for various applications requiring linear motion.
 How to avoid roller bearing failures
How to avoid roller bearing failures
 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd