Enhancing Precision and Efficiency in Mechanical Systems
Introduction:
Linear Guides play a pivotal role in various mechanical systems, enabling smooth and precise linear motion.
From industrial machinery to robotics, linear guides are indispensable components that enhance the efficiency and reliability of these systems.
In this article, we will delve into the world of linear guides, exploring their functionality, types, applications, and the benefits they offer.
Functionality of Linear Guides:
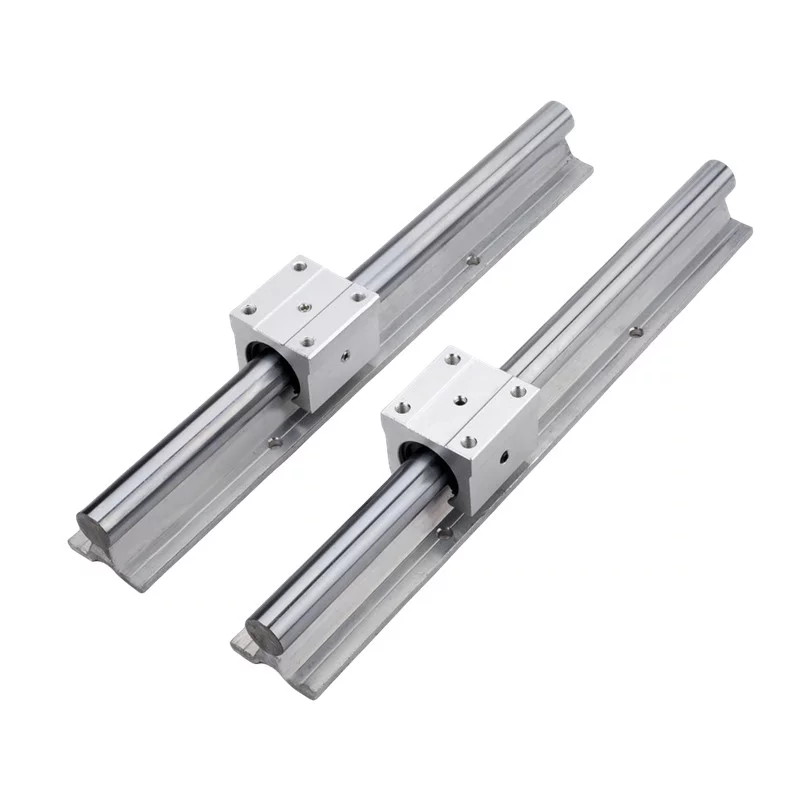
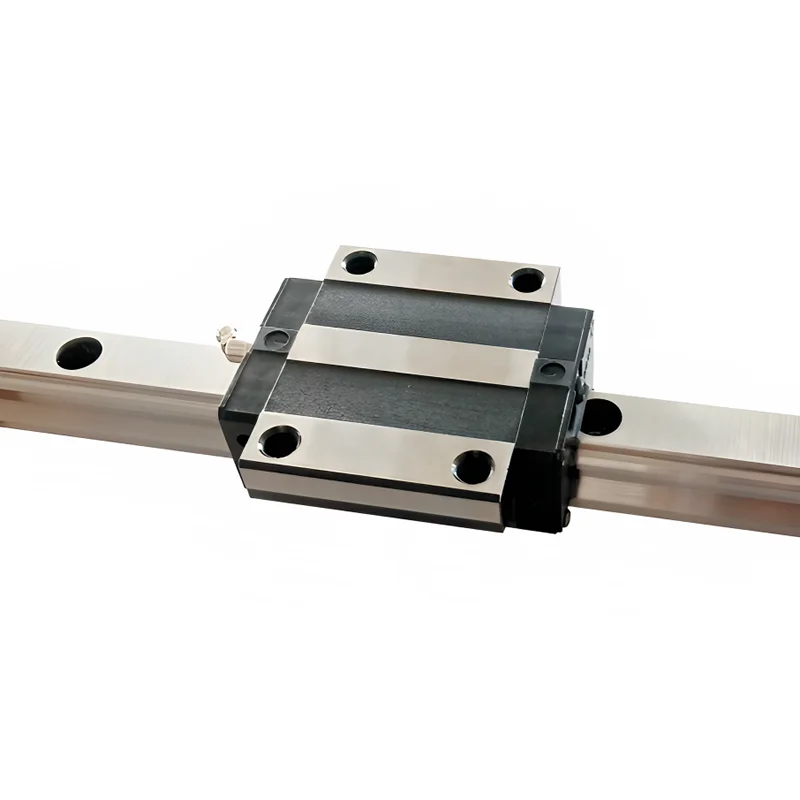
Linear guides, also known as linear motion bearings, provide support and guidance to objects moving linearly.
They consist of two main components: a rail and a carriage. The rail serves as a track, while the carriage houses the rolling elements,
such as balls or rollers, that facilitate smooth motion along the rail.
By minimizing friction and reducing wear, linear guides ensure precise and repeatable linear movement.
Types of Linear Guides:
Ball Guides: Ball guides utilize ball bearings to achieve low friction and high load capacity.
They are ideal for applications that demand high precision and smooth motion, such as CNC machines and high-speed automation systems.
Roller Guides: Roller guides incorporate cylindrical rollers instead of balls, offering higher load capacity and improved rigidity.
These guides are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as machine tools and material handling systems.
Slide Guides: Slide guides feature sliding contact between the rail and carriage, providing excellent shock absorption and vibration damping.
They find applications in industries where smooth and quiet operation is crucial, such as semiconductor manufacturing and medical equipment.
Applications of Linear Guides:
Industrial Machinery: Linear guides are extensively used in industrial machinery, such as milling machines, lathes, and presses.
They enable accurate positioning and smooth movement, ensuring optimal performance and productivity.
Robotics: In robotics, linear guides are critical for the precise and controlled movement of robot arms, gantries, and other robotic components.
They enable robots to perform intricate tasks with accuracy and repeatability.
Automotive Industry: Linear guides find application in automotive manufacturing processes, including assembly lines and robotic welding systems.
They contribute to the efficiency, reliability, and precision required in automotive production.
Benefits of Linear Guides:
Enhanced Precision: Linear guides provide precise linear motion, minimizing errors and ensuring accurate positioning.
This precision is crucial in industries that require high levels of accuracy, such as aerospace and electronics manufacturing.
Increased Efficiency: By minimizing friction and wear, linear guides reduce energy consumption and improve overall system efficiency.
This results in smoother operation, reduced maintenance requirements, and extended component lifespan.
Improved Load Capacity: Linear guides are designed to handle varying load capacities, from light loads to heavy-duty applications.
This versatility allows for the efficient handling of different objects and materials in diverse industries.
Conclusion:
Linear guides are integral components that enable precise and efficient linear motion in mechanical systems.
With their diverse types, applications, and numerous benefits, these guides continue to play a vital role in industries ranging from manufacturing to robotics.
By incorporating linear guides into their systems, engineers can enhance precision, efficiency,
and overall performance, leading to improved productivity and customer satisfaction.
 How to avoid roller bearing failures
How to avoid roller bearing failures
 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd