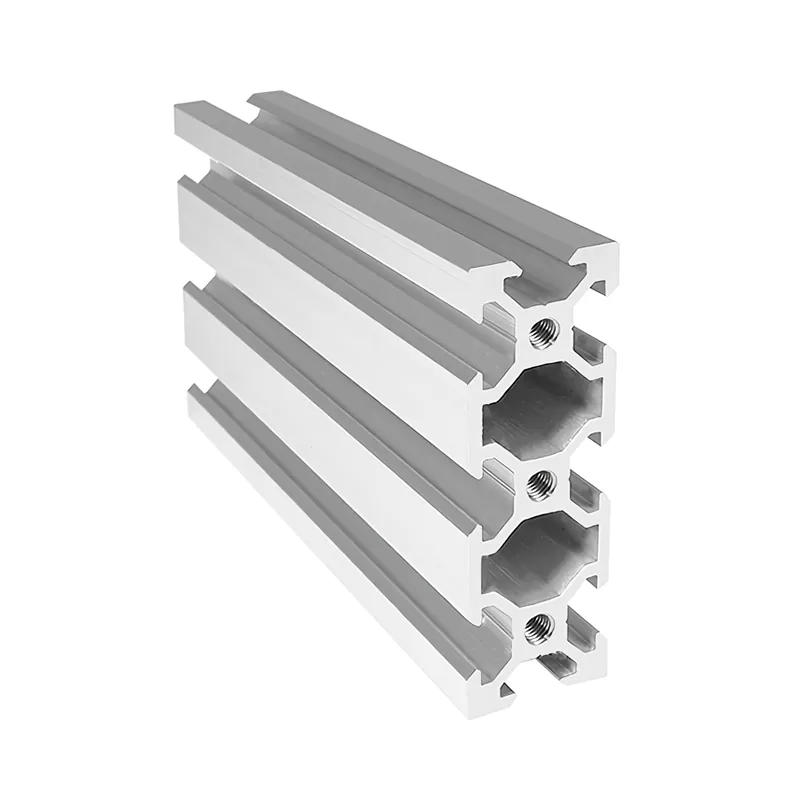
What is the strongest aluminium profile
Aluminium profiles are widely used in construction, machinery manufacturing, transportation, and many other fields. Choosing the right aluminium profile ensures structural stability and longevity. So, which is the strongest aluminium profile? This article will explore this topic from the perspectives of alloy composition, heat treatment state, and section design.
1. Alloy Composition
Aluminium alloys are categorized based on their alloying elements:
1000 Series: Pure aluminium, primarily composed of aluminium (Al), has low strength but excellent corrosion resistance and ductility.
2000 Series: Copper (Cu) is the main alloying element, offering high strength but poor corrosion resistance.
3000 Series: Manganese (Mn) is the primary alloying element, providing good corrosion resistance and moderate strength.
4000 Series: Silicon (Si) is the main alloying element, mainly used in welding materials.
5000 Series: Magnesium (Mg) is the primary alloying element, offering high strength and good corrosion resistance.
6000 Series: Magnesium and silicon are the main alloying elements, offering excellent overall performance and widespread application.
7000 Series: Zinc (Zn) is the primary alloying element, providing the highest strength but poorer corrosion resistance.
Among these, the 7000 series aluminium alloys, such as 7075 aluminium alloy, are known for their exceptional strength, making them suitable for aerospace and high-strength applications.
2. Heat Treatment State
The strength of aluminium alloys is influenced by both their alloy composition and heat treatment state. Common heat treatment states include:
O State: Annealed, offering the lowest strength but the highest ductility.
T4 State: Solution heat-treated and naturally aged, providing moderate strength.
T6 State: Solution heat-treated and artificially aged, offering high strength.
For example, 7075-T6 aluminium alloy, in this heat treatment state, not only provides high strength but also exhibits good toughness and fatigue resistance, making it one of the strongest aluminium profiles available.
3. Section Design
The strength of an aluminium profile depends not only on the material itself but also on its section design. A well-designed section can significantly enhance the load-bearing capacity of the profile. Common section designs include:
Square Tube Profile: Offers good bending and torsion resistance, suitable for frame structures.
H-Beam Profile: Provides high bending resistance, suitable for beam structures.
I-Beam Profile: Lightweight with high strength, suitable for bridges and building structures.
4. Practical Applications
In practical applications, the strongest aluminium profiles are often customized according to specific needs. For instance, the aerospace industry frequently uses 7075-T6 aluminium profiles for aircraft wings and fuselage structures, while the automotive industry employs 6000 series aluminium alloys to manufacture car body frames, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency.
Conclusion
In summary, the strongest aluminium profile is the 7075-T6 aluminium alloy, known for its exceptional strength and overall performance, making it widely used in high-strength demand fields. However, selecting the appropriate aluminium profile requires a comprehensive consideration of the specific application scenario, design requirements, and cost, ensuring structural safety and economic efficiency.
 Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
Why Precision Ball Screws are Vital for Industrial Automation and How to Choose the Right Supplier
 SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
SAIVS Linear Motion Ball Slide Units – Precision and Reliability for Your CNC Needs
 High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
High - Quality T - Slot Aluminum Extrusion Profiles from Ningbo SAIVS Machinery Co., Ltd
 Enhance Industrial Efficiency with Premium Cylinder End Bearings from SAIVS
Enhance Industrial Efficiency with Premium Cylinder End Bearings from SAIVS